How Panchamahabutha Is Corelate With Thridosha

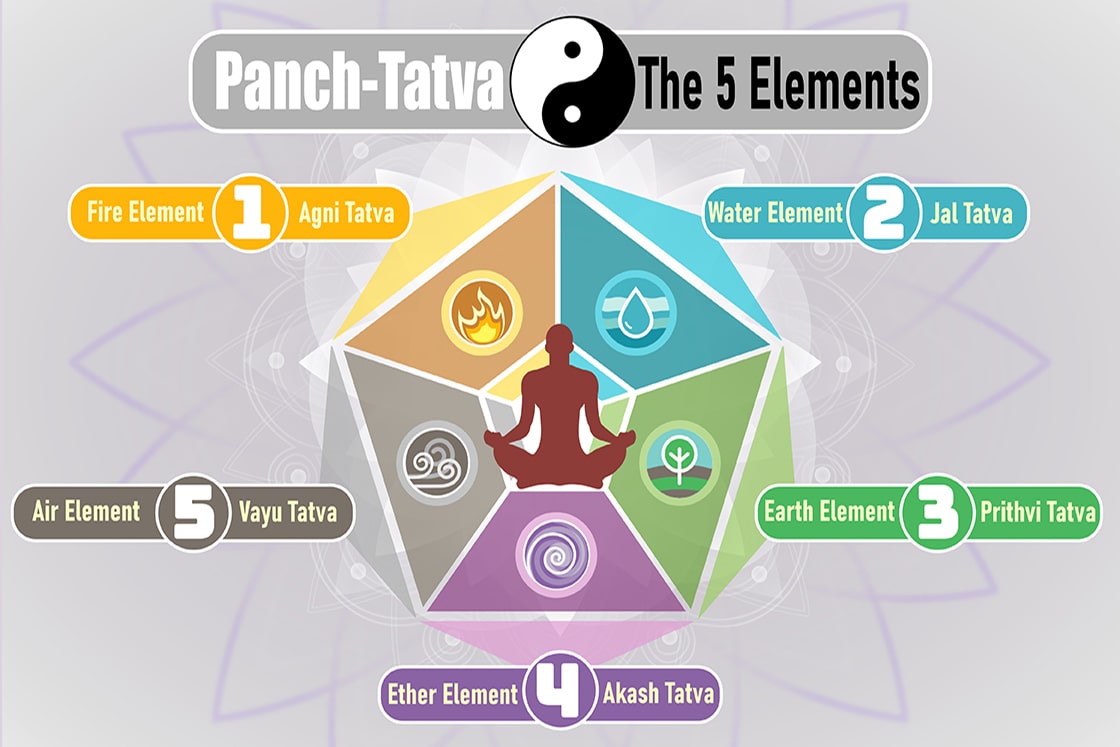
In Ayurveda, the concept of "Panchamahabhuta" (five great elements) is closely related to the Tridosha theory. According to this concept, everything in the universe, including the human body, is composed of five fundamental elements: Ether (Akasha), Air (Vayu), Fire (Agni), Water (Jala), and Earth (Prithvi). Each dosha - Vata, Pitta, and Kapha - is associated with specific combinations of these elements.
Understanding the interplay of Panchamahabhuta with Tridosha provides insights into how the doshas influence the body and mind:
- Vata: Vata is primarily composed of the elements Ether and Air. Ether
represents space and provides the potential for movement, while Air
represents the energy of movement itself. Together, these elements make Vata the force responsible for all types of bodily movements, nerve impulses, and communication within the body. The qualities of mobility and lightness associated with Vata stem from the presence of these elements. - Pitta: Pitta is mainly composed of the elements Fire and Water. Fire
represents the transformative energy responsible for digestion,
metabolism, and various biochemical processes in the body. Water is the lubricating aspect that cools and balances the heat of Fire. The combination of Fire and Water in Pitta gives rise to the qualities of heat and fluidity. - Kapha: Kapha is primarily composed of the elements Water and Earth. Water provides cohesion, fluidity, and nourishment, while Earth represents the solid and stable aspect. The combination of Water and Earth gives Kapha its grounding and stabilizing qualities, as well as its role in providing structure and lubrication in the body.
The balance or imbalance of these Panchamahabhuta within the human body determines an individual’s Prakriti or constitution, which reflects their unique combination of Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. The Tridosha theory suggests that each person is born with a specific proportion of these doshas, which influences their physical and mental characteristics, tendencies, and susceptibilities to imbalances and diseases.
For example:
- A person with a dominant Vata constitution will have more Ether and Air elements in their Prakriti, leading to a slim physique, creative mind, and a tendency for dryness and variability in their health.
- A Pitta-dominant individual will have more Fire and Water elements in their Prakriti, giving rise to a strong metabolism, sharp intellect, and a tendency toward heat-related conditions when imbalanced.
- A Kapha-dominant person will have more Water and Earth elements in
their Prakriti, resulting in a sturdy build, nurturing nature, and a potential
for conditions related to excessive cold and dampness when Kapha is
aggravated.
Ayurveda aims to maintain or restore balance among the doshas and the elements they represent. By understanding the relationship between
Panchamahabhuta and Tridosha, Ayurvedic practitioners develop personalized treatment plans, including lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, herbal remedies, and other therapeutic measures, to support an individual’s overall health and well-being.

 Cart is empty
Cart is empty